In an information-driven world knowledge is one of the most valuable assets an organization can possess. Without a structured approach to managing it, even the most resource-rich businesses can struggle to stay competitive. This is where knowledge management (KM) steps in—a strategic discipline that empowers organizations to create, capture, and use knowledge effectively.
There are many business benefits of knowledge management, including 35% customer support, employee engagement, and employee performance improvement. In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about knowledge management, including its importance, processes, benefits, strategies, and systems that drive success.
What is a knowledge management?
Knowledge management (KM) refers to the structured approach to creating, capturing, organizing, sharing, and utilizing knowledge within an organization. This practice encompasses explicit knowledge, such as documents and policies, and tacit knowledge, which includes employees’ expertise and experiences. Knowledge management ensures that valuable insights are preserved and accessible to drive better decision-making, innovation, and efficiency. It’s more than just storing information; it’s about fostering a culture where knowledge is recognized as a strategic asset. Organizations that invest in knowledge management can reduce information silos, improve cross-functional collaboration, and adapt swiftly to market demands.
Why is knowledge management important?
The importance of knowledge management stems from its ability to address key organizational challenges, with 75% of organizations believing knowledge management is important for their corporate strategy. In our data-driven world employees often spend significant time searching for information or recreating existing solutions. Knowledge management solves this by providing a centralized approach to managing information.
Knowledge management is critical for preserving institutional knowledge, particularly as workforce turnover increases. It ensures that expertise doesn’t walk out the door when employees leave. Knowledge management also fuels innovation by enabling teams to build upon shared ideas, ultimately creating competitive advantages. In customer-facing roles, access to well-organized knowledge can significantly enhance response times and client satisfaction.
Types of knowledge in knowledge management
In knowledge management, understanding the different types of knowledge is crucial for effectively capturing, sharing, and applying insights within an organization. Knowledge can be categorized into three primary types—explicit, tacit, and implicit—which each require different approaches for management.
Explicit knowledge
Explicit knowledge is formal, structured, and easily articulated. It exists in tangible forms such as documents, manuals, policies, and training materials. For example, an employee handbook or a product specification sheet are classic examples of explicit knowledge. Because it is well-documented and systematic, explicit knowledge is straightforward to store in databases, share across teams, and retrieve when needed.
Tacit knowledge
Tacit knowledge represents the skills, insights, and experiences that individuals acquire over time but find difficult to express or document. It’s the deep expertise a senior engineer brings to troubleshooting complex systems or the creativity a designer uses to solve a challenging problem. Tacit knowledge is often shared through mentoring, shadowing, or direct interaction. For instance, a master craftsman teaching an apprentice demonstrates the transfer of tacit knowledge.
Implicit Knowledge
Implicit knowledge lies between explicit and tacit knowledge. It’s not formally documented but is embedded within organizational processes, workflows, and practices. For example, a team that consistently delivers projects efficiently may follow unspoken rules or adopt informal shortcuts that enhance productivity. Unlike tacit knowledge, implicit knowledge can often be inferred and made explicit with careful observation and analysis.
The knowledge management process
Effective knowledge management involves more than just collecting information—it’s about turning knowledge into actionable insights that drive success. The knowledge management process is a dynamic cycle comprising four interconnected stages: knowledge creation, capture, sharing, and application.
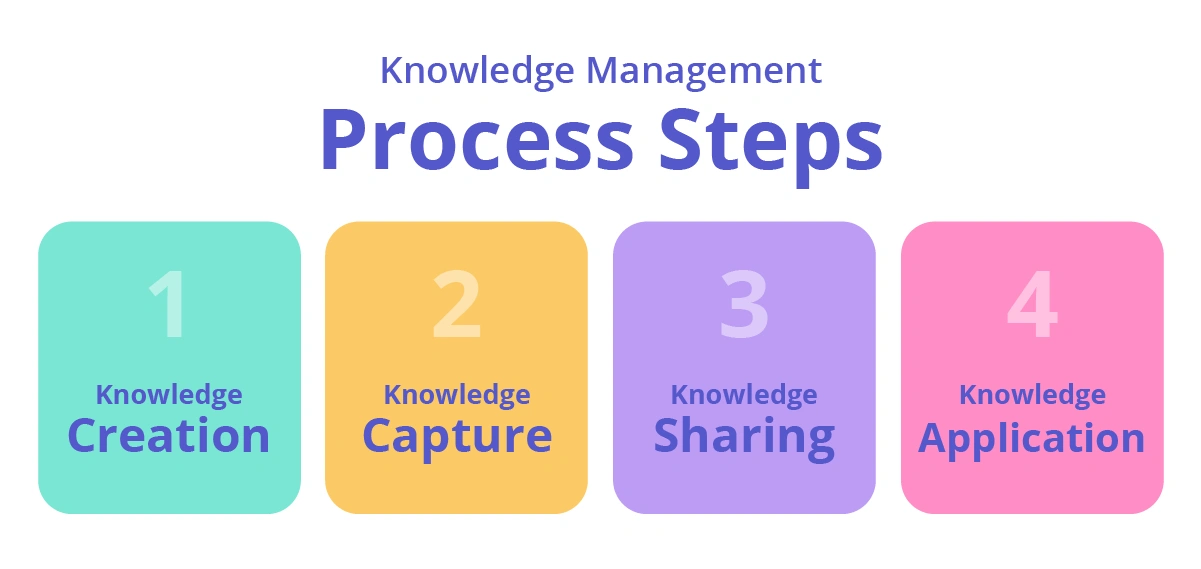
1. Knowledge creation
Knowledge creation is the first step in the knowledge management process and involves generating new insights or ideas. This can occur through various means, such as innovation, brainstorming sessions, or collaborative problem-solving. For example, a team developing a new product might generate ideas through research and discussions, leading to breakthroughs. Encouraging a culture of innovation and open communication is vital to fostering continuous knowledge creation.
2. Knowledge capture
Once new knowledge is created, it must be captured and documented for future use. This can involve conducting interviews with subject matter experts, recording lessons learned during projects, or documenting workflows and best practices. For instance, a retiring engineer may share decades of tacit knowledge through mentoring or video recordings. Effective capture ensures that critical insights are not lost, especially during transitions or workforce changes.
3. Knowledge sharing
Knowledge sharing ensures that valuable information reaches the right people at the right time. This step involves disseminating knowledge through tools like wikis, intranets, collaboration platforms, and team workshops. For example, a sales team might use a centralized knowledge base to share customer success stories and sales strategies. Organizations that prioritize knowledge sharing reduce silos, enhance collaboration, and empower employees with accessible resources.
4. Knowledge application
The ultimate goal of knowledge management is to ensure that knowledge is applied effectively. This means integrating insights into decision-making, improving workflows, and driving innovation. For example, a customer support team might use a knowledge base to resolve issues more efficiently, improving service quality. By embedding knowledge into daily operations, organizations can unlock its full potential and achieve their strategic objectives.
Benefits of knowledge management
Knowledge management offers immense value to organizations, enhancing everything from operational efficiency to employee empowerment. By effectively managing knowledge, businesses can unlock opportunities for innovation, deliver exceptional customer experiences, and reduce costs.
Increased efficiency
Knowledge management eliminates the time wasted searching for information as organizations with effective knowledge management can increase their productivity by at least 20%. By centralizing resources and streamlining access, knowledge management accelerates workflows and decision-making processes. For instance, having an easily accessible knowledge base can help teams resolve issues faster, improving overall productivity and reducing operational delays.
Enhanced innovation
Knowledge management creates a culture of collaboration and idea-sharing that sparks innovation. When employees have access to collective knowledge, they can build upon existing ideas, develop groundbreaking solutions, and improve products or services. For example, brainstorming sessions backed by shared data and insights often lead to creative breakthroughs that drive competitive advantages.
Employee empowerment
85% of employees state the need for better access to knowledge in their organizations. Robust knowledge management systems empower employees by providing them with the tools and information they need to succeed. Access to knowledge boosts confidence, enhances job satisfaction, and encourages continuous learning. For instance, an employee with quick access to procedural guides or expert advice is better equipped to tackle challenges and make informed decisions.
Improved customer experience
Customer-facing teams benefit immensely from knowledge management by using centralized resources to address client inquiries efficiently. A well-structured knowledge base ensures quicker resolutions and personalized support, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty. For example, a support agent using a knowledge management system can resolve issues on the first call, leaving customers with a positive impression.
Cost reduction
By eliminating redundancies and optimizing workflows, knowledge management significantly reduces costs. Organizations save resources by avoiding the duplication of efforts, streamlining standard operating procedures (SOPs), and minimizing errors. For instance, a manufacturing company can use knowledge management to document and standardize production workflows, reducing costly mistakes and ensuring consistent output quality.
Top knowledge management use cases
Knowledge management is a versatile tool with applications across industries. From healthcare to insurance, knowledge management enables organizations to centralize information, improve collaboration, and streamline operations.
Healthcare
In healthcare, knowledge management enables the centralization of patient records, treatment protocols, and clinical guidelines, improving care quality and ensuring compliance with regulations. For example, doctors can access a shared repository of case studies and research papers to make better-informed diagnoses, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Utilities
In the utilities sector, knowledge management helps companies maintain operational efficiency and safety by centralizing technical documentation, maintenance records, and compliance guidelines. For example, a power company can use a knowledge management system to store and share equipment manuals, outage response protocols, and safety standards, enabling technicians to access critical information in real-time during emergencies.
Human Resources (HR)
HR teams leverage knowledge management to streamline onboarding, manage employee training, and ensure compliance with labor laws. For instance, a company can use a centralized knowledge base to provide new hires with step-by-step onboarding instructions, policies, and training resources. Additionally, knowledge management allows HR teams to document and share best practices, ensuring consistency across recruitment and employee management processes.
Information Technology (IT)
In IT, knowledge management plays a critical role in managing knowledge about systems, troubleshooting procedures, and cybersecurity protocols. For example, an IT support team can maintain a knowledge management repository of known issues, FAQs, and resolution guides. This ensures that team members can quickly resolve tickets, minimizing downtime and enhancing user satisfaction. Additionally, knowledge management supports seamless transitions during software upgrades or system migrations.
Government
Knowledge management supports transparency and efficiency in government operations by making policies, public resources, and internal processes accessible. For example, a government agency can use knowledge management to provide citizens with clear guidelines for accessing services, reducing confusion and enhancing public trust.
Best practices for knowledge management
Implementing knowledge management requires more than just tools—it demands strategic planning and adherence to best practices. From gaining leadership support to fostering a knowledge-sharing culture, these practices help organizations maximize the value of their knowledge management initiatives.

Leadership support
Strong leadership is critical for knowledge management success. When executives actively support knowledge management initiatives, it sets the tone for organization-wide adoption. For example, leaders can prioritize knowledge management by allocating resources, promoting its benefits, and encouraging team members to contribute to and utilize knowledge-sharing platforms.
Focus on culture
A knowledge-sharing culture fosters collaboration and innovation. Organizations can encourage this by recognizing and rewarding employees who actively contribute to knowledge management. For instance, celebrating contributions to a company-wide knowledge base can motivate others to share valuable insights and experiences.
Simplify systems
Knowledge management tools should be intuitive and user-friendly to encourage widespread adoption. Complex systems can frustrate users and hinder effectiveness. For example, implementing a straightforward, searchable knowledge base ensures employees can quickly find the information they need without extensive training.
Continuously update
Knowledge assets must remain accurate and relevant to be useful. Organizations should regularly review and refresh their knowledge repositories. For example, outdated compliance policies in a knowledge management system should be promptly updated to reflect new regulations, avoiding costly errors or non-compliance issues.
Train and onboard
Comprehensive training ensures employees understand how to access and contribute to knowledge management systems. For instance, onboarding programs can include tutorials on using collaboration platforms, encouraging new hires to integrate knowledge management into their workflows from the outset.
Strategies for effective knowledge management
A successful knowledge management program depends on well-defined strategies tailored to the organization’s needs. By leveraging technology, promoting inclusivity, and setting measurable goals, businesses can ensure their knowledge management efforts deliver tangible results. Here are some strategies to consider.
Tailored approaches
Effective knowledge management strategies align with an organization’s unique needs. For example, a government agency might focus on compliance-driven knowledge management, while a tech startup prioritizes collaborative innovation tools. Tailoring strategies ensures knowledge management initiatives are practical, relevant, and impactful across industries and teams.
Leverage technology
AI-driven tools enhance knowledge management by automating processes like content tagging, improving search accuracy, and uncovering data insights. For example, predictive search algorithms can help employees find specific documents faster, saving time and enhancing overall system usability.
Promote inclusivity
Inclusivity in knowledge management ensures that knowledge is contributed and accessed by employees at all levels. Organizations can promote this by empowering frontline workers to share insights that improve processes. For example, warehouse staff might document operational shortcuts that boost efficiency.
Set metrics
Measuring knowledge management success helps organizations refine their strategies. Metrics like system usage rates, time saved, or employee satisfaction can indicate effectiveness. For example, tracking how often a knowledge base is accessed can reveal its value to employees and highlight areas for improvement.
Knowledge management systems for business efficiency
Knowledge management systems (KMS) are the backbone of knowledge management initiatives, providing the tools to store, share, and manage information efficiently. From knowledge bases to AI-driven platforms, these systems empower organizations to transform knowledge into actionable insights. Let’s examine the core features of knowledge management system.
Knowledge bases
Knowledge bases centralize information like FAQs, tutorials, and guides, making them accessible to employees and customers. For instance, a company’s internal knowledge base can house troubleshooting guides, enabling IT teams to resolve technical issues more efficiently.
Document management systems
Document management systems secure and organize files, ensuring version control and quick retrieval. For example, legal teams can use these systems to store contracts, ensuring they access the latest versions during negotiations.
Collaboration platforms
Collaboration tools enable real-time knowledge sharing and teamwork. For instance, cross-functional project teams can use these platforms to discuss progress, share documents, and resolve issues without delays.
AI-driven tools
AI-powered knowledge management tools streamline processes like tagging, content recommendations, and behavioral analytics. For example, a customer support chatbot powered by AI can deliver precise solutions by pulling from a dynamic, up-to-date knowledge base.
The role of AI in knowledge management
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing knowledge management by automating processes, enhancing search accuracy, and delivering personalized experiences. As AI technologies evolve, 27% of knowledge management teams state incorporating AI is a top priority as it enables organizations to manage knowledge more effectively and stay ahead in a competitive landscape. Here’s how AI is reshaping knowledge management.
Predict needs
AI can anticipate user needs by analyzing queries and behaviors, suggesting relevant resources. For example, an AI-driven knowledge management system can recommend troubleshooting steps before a support agent asks, reducing resolution times and enhancing productivity.
Enhance search
AI improves search functionality by understanding context, delivering accurate and relevant results. For instance, semantic search capabilities can differentiate between meanings of terms like “lead” (sales vs. material), ensuring users find the right information.
Automate content updates
AI tools can identify outdated content and suggest updates, ensuring knowledge assets remain relevant. For example, an AI system might flag old compliance documents for review when new regulations are detected.
Enable personalization
AI tailors knowledge delivery to individual users, enhancing their experience. For instance, an AI-driven learning management system can recommend training materials based on an employee’s role and skill gaps, fostering growth.
Overcoming challenges in knowledge management
Despite its benefits, implementing KM can come with challenges like resistance to change, information overload, and siloed data (55% of executives report issues with information and data quality). Addressing these hurdles is essential to ensure the success and longevity of knowledge management programs. Let’s discuss strategies to overcome these obstacles.
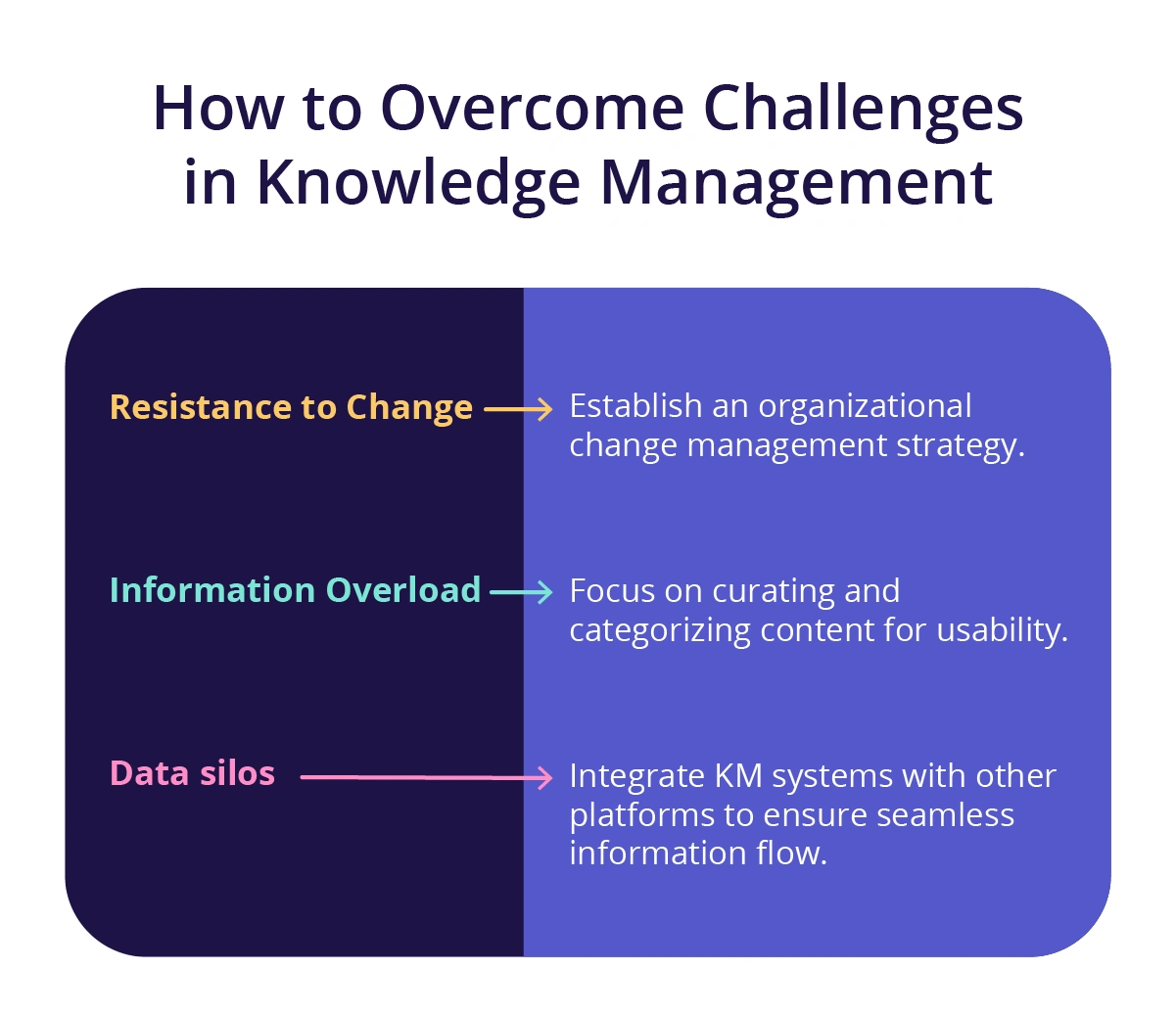
Resistance to change
Resistance to adopting knowledge management systems is common, particularly when employees are accustomed to traditional methods. Overcoming this requires change management strategies like highlighting the benefits of knowledge management and offering training. For example, emphasizing how knowledge management simplifies workflows can motivate teams to embrace the change.
Information overload
Too much information can overwhelm users and reduce knowledge management system effectiveness. Organizations should focus on curating and categorizing content for usability. For example, using filters and tagging systems ensures employees quickly find the exact resources they need without sifting through irrelevant data.
Data silos
Silos hinder knowledge sharing and collaboration. Bridging these requires integrating knowledge management systems with other platforms to ensure seamless information flow. For example, connecting a CRM system with a knowledge base enables sales and support teams to share insights, improving customer service.
Getting started with knowledge management in your organization
Knowledge management is more than a process; it’s a strategic imperative for organizations striving to innovate, adapt, and excel. By understanding knowledge management’s importance, leveraging the right strategies, and embracing advanced systems, businesses can unlock the full value of their knowledge assets.
Visit our features page to learn more about how your organization can use knowledge management to improve customer satisfaction, boost operational efficiency, and drive innovation.



