Organizations seeking to maintain productivity and continuous improvement must ensure the effective transfer of knowledge. Knowledge transfer involves the movement of valuable knowledge, skills, and expertise from one person, team, or department to another. Successful knowledge transfer enhances productivity, accelerates learning, and improves decision-making within an organization.
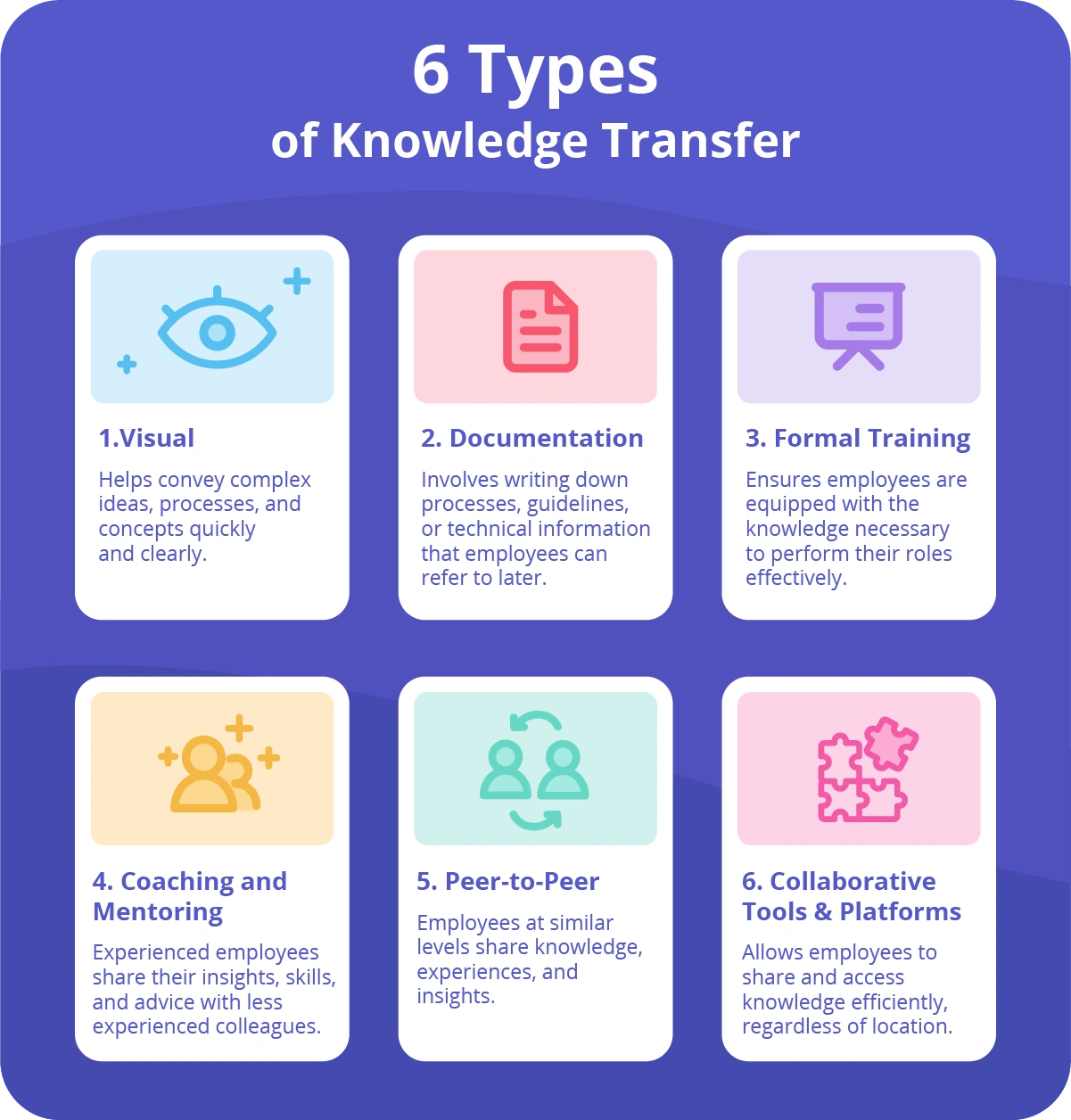
While the methods of knowledge transfer can vary depending on the nature of the information being shared and the organization's culture, the following are some of the most common types of knowledge transfer within an organization: visual knowledge transfer, documentation, formal training, mentoring/coaching, peer-to-peer transfer, and collaborative tools.
Visual knowledge transfer
Visual knowledge transfer involves sharing information through visual representations, such as charts, diagrams, infographics, videos, or other visual aids. This method helps convey complex ideas, processes, and concepts quickly and clearly since humans process visuals 60,000 times faster than text and 90% of information transmitted to the brain is visual. Visual aids are especially helpful in environments where concepts need to be explained in a way that is easy to understand at a glance.
Methods of visual knowledge transfer
-
Flowcharts: Used to represent processes or complex concepts in a simplified, visually appealing way.
-
Videos and tutorials: Providing visual demonstrations or recorded sessions can show how something is done, particularly useful for technical or procedural knowledge.
-
Diagrams: Often used to explain workflows, systems, or hierarchies within an organization.
-
Whiteboarding: Collaborative sessions where ideas are drawn out visually, allowing teams to brainstorm and share knowledge in real-time.
Benefits of visual knowledge transfer
-
Speeds up understanding and retention of information.
-
Reduces cognitive overload by simplifying complex information.
-
Engages employees, especially those who are visual learners.
Challenges of visual knowledge transfer
-
Require regular updates to remain relevant.
-
Needs tools, time and resources for creating professional visuals.
Documentation knowledge transfer
Documentation is a traditional method for knowledge transfer. It involves writing down processes, guidelines, or technical information that employees can refer to later. Well-organized documentation can preserve institutional knowledge, making it easily accessible for current and future employees.
Methods of documentation knowledge transfer
-
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Written guidelines that provide step-by-step instructions on performing tasks or processes.
-
User manuals: Manuals that describe how to use specific tools, systems, or software within the organization.
-
Knowledge repositories: Centralized digital libraries where employees can find important documents, case studies, templates, and FAQs.
-
Reports and white papers: Detailed, structured documents that provide in-depth analysis, research findings, or project outcomes.
Benefits of documentation knowledge transfer
-
Provides a standardized way to share important knowledge across the organization.
-
Enables employees to refer to information when needed, promoting consistency.
-
Can be stored and organized for easy retrieval.
Challenges of documentation knowledge transfer
-
Maintaining up-to-date documentation can be time-consuming.
-
May not be easily understood by all employees, especially those who are new to a process or role.
-
Too much documentation can overwhelm employees and lead to information overload.
-
As business processes evolve documentation can quickly become outdated.
Formal training knowledge transfer
Formal training is an organized, systematic method of transferring knowledge to employees. It can be delivered through in-person workshops, online courses, seminars, or certifications. Formal training ensures that employees are equipped with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their roles effectively.
Methods of formal training
-
Classroom training: Traditional instructor-led training in a classroom setting, often for groups of employees.
-
Scenario-based learning: Involves presenting employees with realistic situations or problems that they may encounter in their roles.
-
E-Learning platforms: Online courses, webinars, and virtual workshops where employees can learn at their own pace, often with a structured curriculum.
-
Workshops and seminars: Interactive sessions focusing on specific topics or skills, often with expert instructors leading discussions or activities.
Benefits of formal training
-
Provides structured learning and skill development.
-
Ensures all employees receive consistent information.
-
Scalable across large organizations with multiple employees.
Challenges of formal training
-
Time-consuming and can be costly to organize.
-
May not address individual learning styles or immediate knowledge gaps.
-
Needs continuous updates to remain relevant.
Coaching and mentoring knowledge transfer
Coaching and mentoring are personalized, one-on-one approaches to knowledge transfer. In these settings, experienced employees share their insights, skills, and advice with less experienced colleagues to help them develop both professionally and personally.
Methods of coaching and mentoring
-
Coaching: A coach helps employees improve their performance, develop specific skills, and work through challenges, often on a short-term basis.
-
Mentoring: A mentor provides long-term guidance and advice, helping employees grow by sharing their personal experiences and knowledge.
-
Shadowing: New employees or those seeking new skills observe a more experienced colleague performing tasks to learn how things are done in real time.
-
Feedback sessions: Regular one-on-one meetings between supervisors and employees to discuss performance, share advice, and set developmental goals.
Benefits of coaching and mentoring
-
Encourages personal and professional development.
-
Promotes strong relationships between employees and senior staff.
-
Transfers tacit knowledge that can’t be easily documented or formalized.
Challenges of coaching and mentoring
-
Success depends on the skills and availability of the mentor/coach.
-
Requires time and commitment from both parties.
-
May be difficult to scale to larger groups.
Peer-to-peer knowledge transfer
Peer-to-peer knowledge transfer occurs when employees at similar levels share knowledge, experiences, and insights. This method encourages collaboration, learning from one another, and fostering a culture of knowledge sharing.
Methods of peer-to-peer knowledge transfer
-
Learning groups: Small groups of employees who meet regularly to discuss specific topics, challenges, or knowledge areas.
-
Cross-training: Employees are trained in multiple roles or functions within the organization, so they can share knowledge and skills with others.
-
Collaborative projects: Employees work together on projects, exchanging ideas, best practices, and knowledge along the way.
-
Job rotation: Employees periodically switch roles within the organization, gaining new perspectives and sharing their knowledge with others in the process.
Benefits of peer-to-peer knowledge transfer
-
Promotes a culture of continuous learning and collaboration.
-
Allows employees to share real-world knowledge and practical insights.
-
Enhances teamwork and collective problem-solving.
Challenges of peer-to-peer knowledge transfer
-
Knowledge sharing may not be consistent or well-documented.
-
Peer relationships can introduce biases or incomplete knowledge sharing.
-
Not everyone may be comfortable with sharing their expertise or learning from peers.
Collaborative tools and platforms knowledge transfer
The rise of digital tools and platforms has transformed how knowledge is transferred within organizations. These tools facilitate real-time communication, information sharing, and collaboration, allowing employees to share and access knowledge efficiently, regardless of location.
Methods of collaborative tools and platforms knowledge transfer
-
Enterprise social networks: Platforms allow employees to exchange information, ask questions, and share updates in real-time.
-
Document sharing platforms: Cloud-based tools enable teams to collaboratively edit and store documents.
-
Project management tools: Software facilitates team collaboration, task assignment, and knowledge sharing related to specific projects.
-
Internal knowledge bases: Platforms that allow employees to create and share process guides for others in the organization.
Benefits of collaborative tools and platforms knowledge transfer
-
Facilitates real-time communication and collaboration, especially for remote teams.
-
Provides easy access to shared resources and knowledge.
-
Promotes transparency and the sharing of best practices.
-
Ensures knowledge is not lost after employees depart.
Challenges of collaborative tools and platforms knowledge transfer
-
Knowledge sharing can be unorganized or fragmented.
-
Employees may become overwhelmed by the volume of content.
-
Potential for knowledge silos if certain groups do not actively share or engage.
Successfully transfer knowledge in your organization
Effective knowledge transfer is vital for organizational success. The various types of knowledge transfer—visual, documentation, formal training, coaching, peer-to-peer transfer, and collaborative tools—each offer unique benefits and challenges. Choosing the right method depends on the nature of the knowledge being transferred, the organizational context, and the needs of employees. By leveraging a combination of these methods, organizations can ensure that valuable knowledge is shared effectively, promoting continuous learning and operational efficiency.
Visit our features page to learn more about how we can help you implement a successful knowledge transfer strategy to empower employees and support long-term organizational growth.



