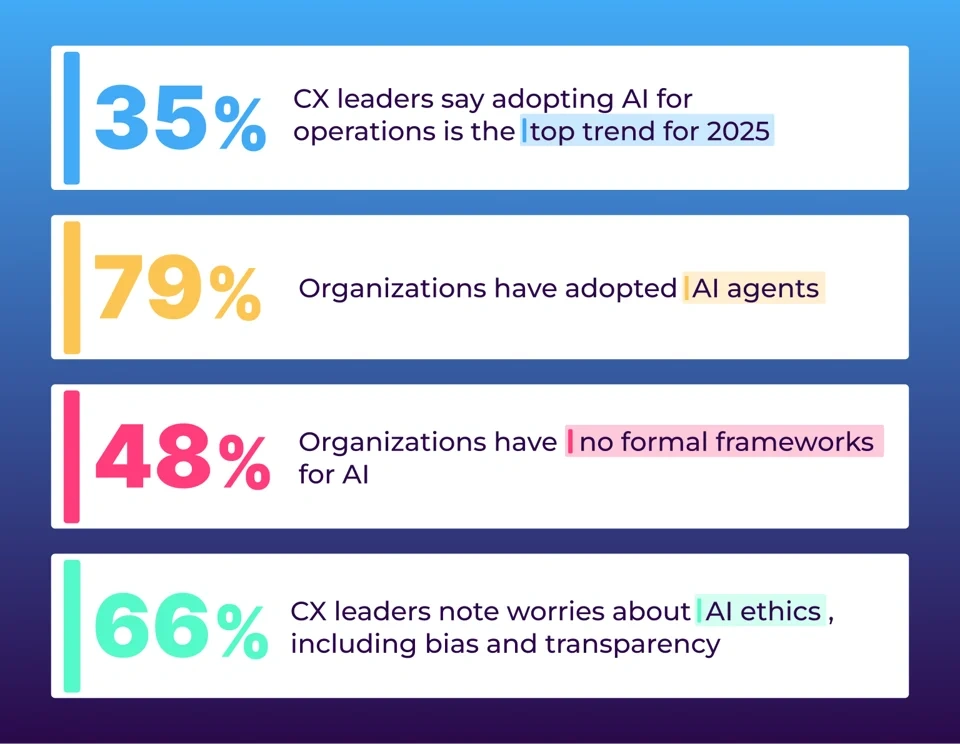
Artificial intelligence is moving beyond simple automation into systems that can act and adapt on their own, with 79% of organizations having adopted AI agents and 96% planning to expand their usage in 2025.
Two key terms in this space—agentic AI and AI agents—are often confused but serve very different purposes. Knowing the difference helps businesses decide where to invest: AI agents excel at assisting with tasks like customer support, while agentic AI drives autonomous operations and decision-making. Used together, they can cut costs, boost operational efficiency, and improve customer service.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems that act with autonomy, making decisions and taking actions toward a goal with minimal human input. Unlike simple automations, agentic AI can adapt, plan, and execute across workflows.
For example, an agentic AI could:
-
Analyze customer service tickets, prioritize urgent issues, and automatically assign tasks to the right team member.
-
Optimize a supply chain by identifying delays, rerouting shipments, and adjusting inventory levels in real-time.
-
Conduct research, summarize findings, and prepare recommendations without instructions from humans.
In 2025, AI-powered technologies for operations, including agentic AI, ranked as the #1 trend in CX, showing how quickly it’s reshaping the business landscape.
What are AI agents?
AI agents are specialized applications of AI built to complete specific tasks or assist humans in real time. For example, chatbots, copilots, or support assistants that:
- Automate responses to customer questions so humans can focus on high-value, empathetic interactions
- Provide recommendations based on context
- Collaborate with human workers by managing repetitive tasks and knowledge retrieval
AI agents are evolving rapidly:
-
From reactive tools that only respond when prompted, to proactive assistants that anticipate needs
-
From generic suggestions to context-aware recommendations, tailoring responses based on a user’s environment, preferences, or historical data
-
From task execution to enhancing decision-making, helping humans navigate complex workflows and optimize outcomes
As they become more sophisticated, AI agents are bridging the gap between automation and human collaboration, effectively acting as extensions of the workforce. They don’t just complete tasks, they enhance human productivity, accuracy, and responsiveness.
How is agentic AI different from AI agents?
While both agentic AI and AI agents fall under the umbrella of artificial intelligence, they serve distinct purposes and operate in different ways. Understanding the differences can help businesses choose the right AI solution for their needs.
Agentic AI:
-
Operates autonomously, making decisions and taking actions without constant human guidance
-
Is goal-driven, able to plan and execute multi-step processes to achieve broader objectives
-
Can adapt dynamically to changing conditions, learning from outcomes to improve future decisions
Examples: AI systems that optimize supply chains, prioritize customer cases across multiple departments, or autonomously manage complex workflows
AI Agents:
-
Are task-focused and designed to support humans or automate specific activities
-
Typically operate within defined boundaries, handling tasks rather than broad goals
-
Are often interactive and context-aware, providing recommendations, insights, or direct responses in real time
Examples: Customer service chatbots, sales copilots, or internal workflow assistants
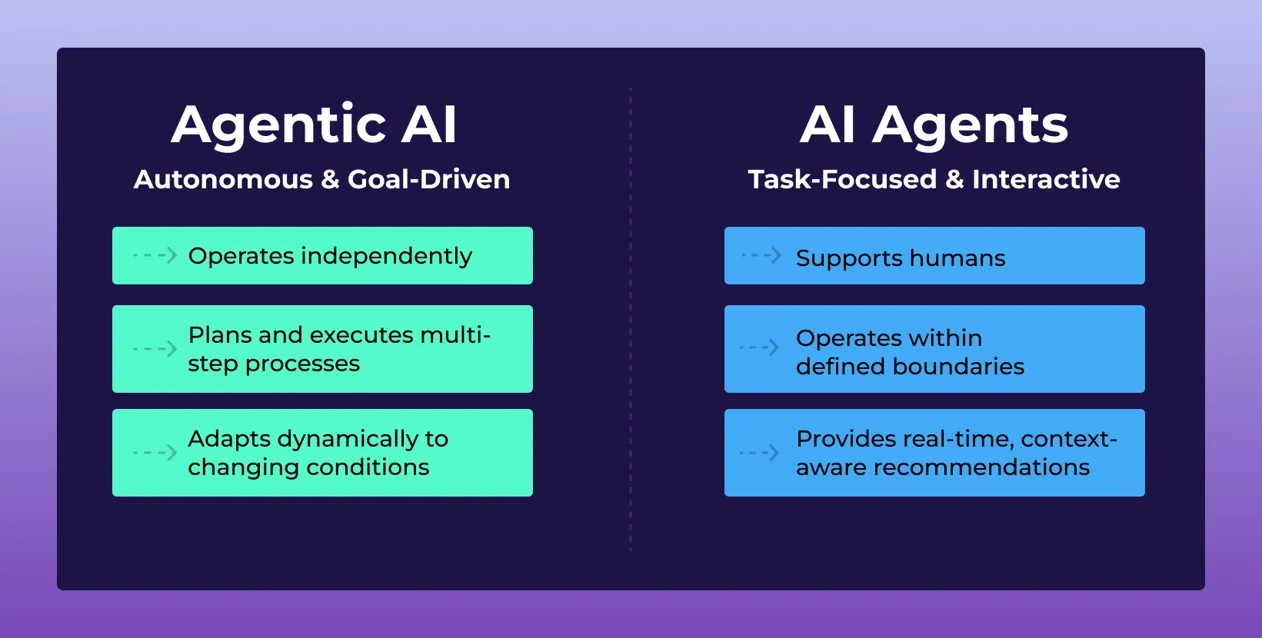
Here’s a simple breakdown:
-
Agentic AI: Autonomous, goal-driven systems that act independently across processes.
-
AI Agents: Task-focused assistants designed to augment or replace manual activities.
Think of agentic AI as the brains that can strategize and execute, while AI agents are the hands and voice that directly engage with users or processes.
Why should businesses care about agentic AI vs AI agents?
Understanding the distinction between agentic AI and AI agents is more than just a technical detail, it can directly impact business performance, customer experience, and operational efficiency. Both types of AI drive value, but in different ways:
Agentic AI drives operational efficiency:
-
By autonomously managing complex workflows, agentic AI reduces manual effort and streamlines processes across departments.
-
It can identify bottlenecks, prioritize tasks, and optimize resource allocation, freeing human teams to focus on higher-value work.
Example: Agentic AI systems can manage end-to-end supply chain operations, from procurement to delivery, optimizing for cost and efficiency.
AI agents enhance customer and employee experiences:
-
AI agents interact directly with users, providing quick, contextual responses and personalized recommendations.
-
They support self-service, reduce response times, and improve satisfaction for both customers and employees.
-
They automate tedious, error-prone tasks: like data entry, record updates, and balance calculations.
Example: AI agents can assist customers by answering frequently asked questions, troubleshooting issues, and providing product recommendations.
Agentic AI and AI agents complement each other: one drives efficiency and decision-making behind the scenes, while the other enhances interactions and outcomes at the user level. Companies that understand and leverage both are better positioned to scale operations, improve CX, and accelerate growth.
What are the challenges with adopting agentic AI and AI agents?
While AI offers tremendous potential, there are several risks businesses must address to ensure safe and effective adoption:
-
Lack of governance: 48% of organizations have no formal frameworks for generative or agentic AI, increasing the chance of errors and inconsistent outcomes.
-
Customer concerns: 66% of CX leaders note worries about AI ethics, including bias and transparency.
-
Data and knowledge gaps: Fragmented systems and poor knowledge foundations limit AI effectiveness and accuracy.
-
Amplified mistakes: Without centralized, validated knowledge, AI can propagate errors and create compliance risks. More than 40% of agentic AI projects are expected to be canceled by the end of 2027 due to insufficient risk controls.
Strong knowledge governance ensures AI operates safely, reliably, and ethically, while reducing risk.
Learn more about why knowledge governance is essential for safe AI adoption →
How can businesses optimize AI adoption?
Maximizing the impact of AI requires a thoughtful approach. Focusing on key strategies helps businesses implement AI responsibly, drive value, and improve operational efficiency.
-
Build clear AI governance models to ensure ethical and transparent use.
-
Centralize access to knowledge so AI has clean, accurate data to work with.
-
Choose a starter use case (like customer support) to prove ROI quickly.
-
Equip teams with training on responsible AI use and change management.
For businesses ready to act, AI can streamline repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and support smarter decision-making, all while maintaining customer trust.
Where should businesses start?
Agentic AI and AI agents are not competing technologies; they’re complementary. Together, they enable smarter operations and better customer experiences.
But success depends on data readiness, governance, and the right use cases. Businesses that invest in these foundations now will be better positioned to scale AI responsibly and profitably.
Ready to see how automation and AI can improve efficiency in your organization?