The ability to effectively manage and leverage knowledge is crucial for any organization aiming to stay competitive. Knowledge management (KM) encompasses the strategies and practices used to identify, create, represent, distribute, and enable the adoption of insights and experiences.
There are many business benefits from knowledge management, including 35% customer support, employee engagement, and employee performance improvement.
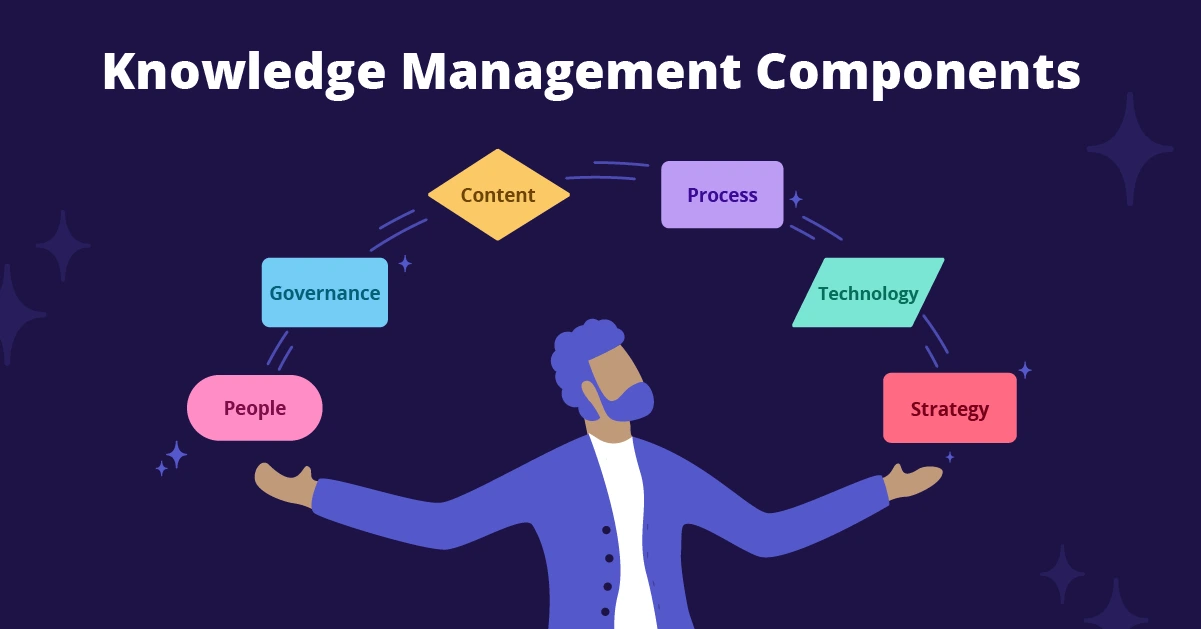
This article explores the six key components of knowledge management: people, governance, content, process, technology, and strategy, detailing how they interconnect to form a robust knowledge management system.
What are knowledge management components?
Knowledge management components are the fundamental building blocks of a knowledge management system, encompassing the various elements required to effectively capture, store, share, and utilize knowledge within an organization.
The six fundamental components are:
- People – those who create, share, and utilize knowledge.
- Governance – policies and standards guiding KM activities.
- Content – the knowledge itself, including data, information, and insights.
- Process – workflows for capturing, sharing, and applying knowledge.
- Technology – tools and platforms that enable KM.
- Strategy – aligning KM initiatives with overall business objectives.
Each plays a distinct role:
- People focus on the human aspect of knowledge sharing and creation.
- Governance ensures that policies and standards are in place to guide KM activities.
- Content involves the organization and maintenance of knowledge itself.
- Process refers to the workflows and methodologies for managing knowledge.
- Technology provides the tools and platforms to support KM activities.
- Strategy aligns KM initiatives with the organization's broader business goals.
Together, these components create a structured and efficient system for managing organizational knowledge.
Why are knowledge management components important?
Knowledge management components are crucial because they provide a comprehensive framework for managing an organization's intellectual assets, ensuring that knowledge is systematically handled and effectively utilized.
By focusing on these components, organizations can foster a culture of continuous learning and innovation, enhance decision-making, and improve operational efficiency.
Effective governance ensures compliance and alignment with strategic goals, while robust processes and technology streamline the flow of knowledge. Having a clear strategy ensures that KM efforts are purposeful and directly contribute to achieving business objectives.
- They provide a framework for systematically managing intellectual assets.
- Help foster a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
- Improve operational efficiency and decision-making.
- Reduce the risk of knowledge loss and maintain a competitive edge.
How does each KM component work?

People
People are at the core of knowledge management, as they create, share, and utilize knowledge within an organization. This component focuses on fostering a collaborative culture where knowledge sharing is encouraged and valued.
Key roles include knowledge workers who generate and use knowledge, knowledge managers who oversee KM initiatives, and subject matter experts (SMEs) who provide deep expertise and guidance.
Building a knowledge-friendly culture involves promoting open communication, teamwork, and providing incentives for knowledge sharing and innovation. Additionally, continuous training and development are essential to keep employees' skills and knowledge up to date.
Mentoring programs can facilitate the transfer of tacit knowledge from experienced employees to newer ones, ensuring that valuable insights are retained and disseminated throughout the organization. Ultimately, the people component is about leveraging human capital to enhance organizational learning and performance.
Roles
- Knowledge Workers: Employees who create and use knowledge in their day-to-day tasks.
- Knowledge Managers: Individuals responsible for overseeing KM initiatives and ensuring the smooth flow of knowledge.
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Specialists with deep expertise in specific areas who provide valuable insights and guidance.
Governance
Governance in knowledge management involves establishing procedures, policies, and standards to guide the management of knowledge within an organization. Effective governance ensures that KM activities align with organizational goals and comply with relevant regulations.
This component includes defining knowledge policies that specify what constitutes critical knowledge, how it should be managed, and who is responsible for it. Data privacy and security are also crucial, ensuring that KM practices safeguard sensitive information and comply with data protection regulations.
A KM steering committee, typically composed of senior leaders, provides oversight and strategic direction, while compliance officers ensure adherence to legal and regulatory requirements.
Performance measurement is another critical aspect, involving the establishment of key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the effectiveness of KM initiatives. Regular audits and reviews help maintain compliance and drive continuous improvement, ensuring that KM practices remain effective and aligned with business objectives.
Performance Measurement
- Metrics and KPIs: Establishing key performance indicators to measure the effectiveness of KM initiatives.
- Audits and Reviews: Conducting regular audits to ensure compliance with KM policies and continuous improvement.
Content
Content is the substance of knowledge management, encompassing the data, information, and knowledge that flow through an organization. Managing content effectively involves organizing, categorizing, and maintaining it to ensure it is accessible and useful.
Content creation and acquisition involve gathering information from both internal sources, such as documents and reports, and external sources like industry research and databases.
Proper content organization requires a structured system of taxonomy and classification to categorize and index knowledge for easy retrieval, while metadata enhances searchability and context.
Maintenance of content is equally important, involving regular updates to keep information relevant and accurate, and archiving outdated data. Version control is crucial to manage multiple iterations of documents, ensuring that changes and updates are tracked. Ultimately, the content component ensures that knowledge is systematically managed, making it readily available for decision-making and innovation.
Content Creation
- Internal Sources: Documents, reports, databases, and other materials generated within the organization.
- External Sources: Information gathered from external databases, industry reports, and market research.
Content Maintenance
- Updating and Archiving: Regularly updating content to ensure its relevance and accuracy, and archiving outdated information.
- Version Control: Managing multiple versions of documents to keep track of changes and updates.
Process
Processes in knowledge management refer to the workflows and methodologies used to manage knowledge throughout its lifecycle. These processes ensure that knowledge is effectively captured, stored, shared, and utilized.
Currently, most organizations depend on 10+ platforms for documenting processes or sharing information.
Knowledge capture involves systematically documenting tacit knowledge from employees through methods such as interviews, surveys, and observation.
Creating centralized knowledge repositories helps in storing and managing these knowledge assets efficiently.
Knowledge sharing is facilitated through communities of practice, where individuals with common interests can collaborate and share insights, and through various collaboration tools like intranets, wikis, and social platforms.
Knowledge utilization focuses on embedding knowledge into business processes to ensure it is applied in decision-making and operations.
Continuous learning and innovation are driven by leveraging the accumulated knowledge to improve practices and develop new solutions. The process component ensures that knowledge flows seamlessly across the organization, enhancing efficiency and fostering a culture of knowledge-driven growth.
Knowledge Capture
- Documentation: Systematically documenting tacit knowledge from employees through interviews, surveys, and observation.
- Knowledge Repositories: Creating centralized repositories such as a knowledge base to store and manage knowledge assets.
Knowledge Utilization
- Integration into Operations: Embedding knowledge into business processes to ensure it is used in decision-making and operations.
- Continuous Improvement: Leveraging knowledge to drive learning initiatives and foster innovation.
Technology
Technology is a crucial enabler of knowledge management, providing the tools and platforms needed to capture, store, share, and utilize knowledge effectively—yet half of executives agree knowledge remains trapped in silos.
Key technological components include knowledge management systems (KMS), content management systems (CMS), and document management systems (DMS), which help in creating, managing, and tracking digital content.
Collaboration and communication tools such as intranets, portals, and social media platforms facilitate the seamless exchange of knowledge among employees.
Advanced technologies like data mining and analytics uncover patterns and insights from large datasets, while artificial intelligence (AI) enhances search capabilities and provides personalized knowledge recommendations.
Implementing these technologies helps streamline KM processes, making knowledge more accessible and actionable. Technology not only supports the day-to-day activities of knowledge management but also drives innovation by enabling new ways to capture and leverage knowledge, ultimately contributing to the organization’s strategic objectives.
Knowledge Management Systems (KMS)
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Platforms for creating, managing, and publishing digital content.
- Document Management Systems (DMS): Systems for storing, managing, and tracking electronic documents.
Data and AI
- Data Analytics: Techniques for analyzing large datasets to uncover patterns and insights.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven tools for automating knowledge capture, enhancing search capabilities, and providing personalized knowledge recommendations.
Strategy
A well-defined knowledge management strategy aligns KM initiatives with the organization’s overall business objectives, ensuring that KM efforts are purposeful and add value.
This component involves articulating a clear vision for knowledge management that aligns with the organization’s mission and values, and setting specific, measurable objectives that support business goals.
Integrating KM with business processes ensures that knowledge management activities are embedded in the organization’s operations and contribute to strategic initiatives.
Effective change management practices are crucial to facilitate the adoption of KM processes and technologies, ensuring smooth transitions and employee buy-in.
Resource allocation is another critical aspect, involving budgeting and funding to support KM initiatives and attracting, retaining, and developing talent with the necessary skills. By aligning KM with strategic goals, organizations can enhance decision-making, drive innovation, and maintain a competitive edge in a dynamic business environment.
Objectives
- Knowledge Management Vision: Articulating a clear vision for knowledge management that aligns with the organization’s mission and values.
- Strategic Goals: Setting specific, measurable objectives for KM initiatives that support business goals.
Integration with Business Processes
- Alignment with Business Strategy: Ensuring that KM activities support and enhance the organization’s strategic initiatives.
- Change Management: Implementing change management practices to ensure smooth adoption of KM processes and technologies.
In Summary: The 6 Components of Knowledge Management
The six components of knowledge management—people, governance, content, process, technology, and strategy—form the foundation of an effective KM system. Each plays a distinct role:
- People create and share knowledge.
- Governance provides structure and accountability.
- Content ensures knowledge is accurate, organized, and accessible.
- Processes define how knowledge flows through the organization.
- Technology supports the capture, storage, and sharing of knowledge.
- Strategy aligns KM initiatives with business goals.
When these components work together, organizations can reduce knowledge loss, improve decision-making, and create a scalable system for continuous learning and operational efficiency.
The key components of knowledge management in your business
The six components of knowledge management—people, governance, content, process, technology, and strategy—are interdependent elements that collectively form a comprehensive KM framework.
By focusing on these components, organizations can create a culture of knowledge sharing, ensure compliance with policies and regulations, effectively manage their knowledge assets, streamline workflows, and leverage technology to support KM initiatives.
To learn more about how your business can benefit from the components of knowledge management by simplifying processes with a visual knowledge base, explore our product features.